- The name ‘India’ is derived from the River Indus, the valleys around which were the home of the early settlers.
- Indians established Harappan culture in Sindhu Valley (Indus Valley Civilization) nearly 5,000 years ago
- Chess was invented in India.
- Algebra, Trigonometry and Calculus are studies, which originated in India.
- The ‘Place Value System’ and the ‘Decimal System’ were developed in India in 100 B.C
- Ayurveda, a natural system of medicine, originated in India more than 2,500 years ago.
- Varanasi, was called “the Ancient City”, continuously inhabited city in the world today.
- Yoga has its origins in India and has existed for over 5,000 years.
- The Indian peninsula is separated from mainland Asia by the Himalayas.
- India is surrounded by the Bay of Bengal in the east, the Arabian Sea in the west, and the Indian Ocean to the south. The north-south extent from Kashmir to Kanyakumari measures about 3,200 km. The east-west extent from Arunachal Pradesh to Kochi measures about 2,900 km.
- The Tropic of Cancer (23°30′ N) passes almost halfway through the country. India extends between 8°4′ N and 37°6′ N, Latitude south to north, and 68° 7’E and 97° 25’E longitudes west to east.
- India has an area of about 3, 28 million sq. km.
- India is the largest democracy in the world, the 7th largest Country in the world.
- There are seven countries that share land boundaries with India, Afghanistan and Pakistan to the north-west; China, Bhutan and Nepal to the north; Myanmar to the east; and Bangladesh to the east of West Bengal. Sri Lanka is separated from India by a narrow channel of sea, formed by Palk Strait

- India is a Sovereign Socialist Secular Democratic Republic with a Parliamentary form of government
- Delhi is the Capital City of India
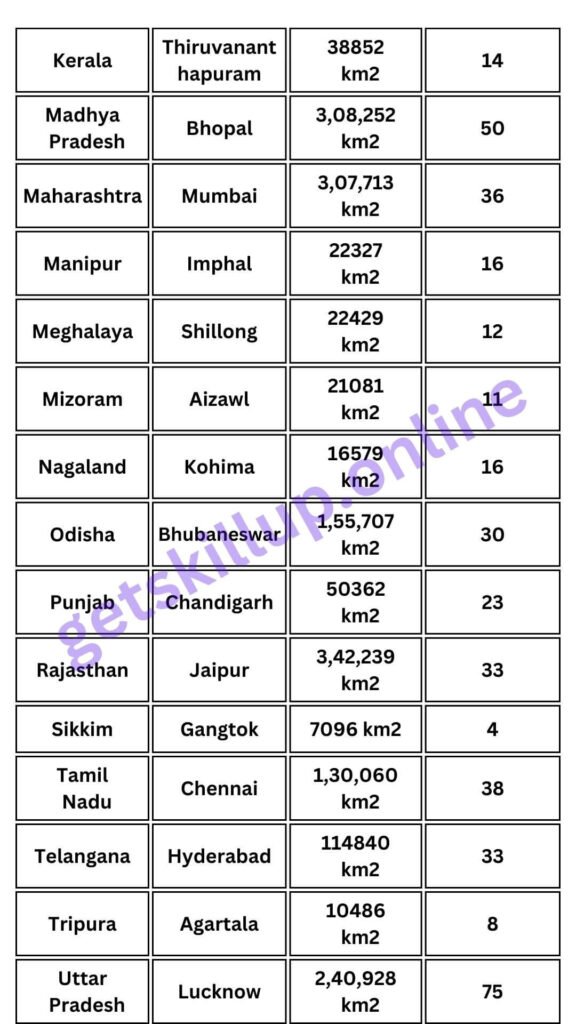
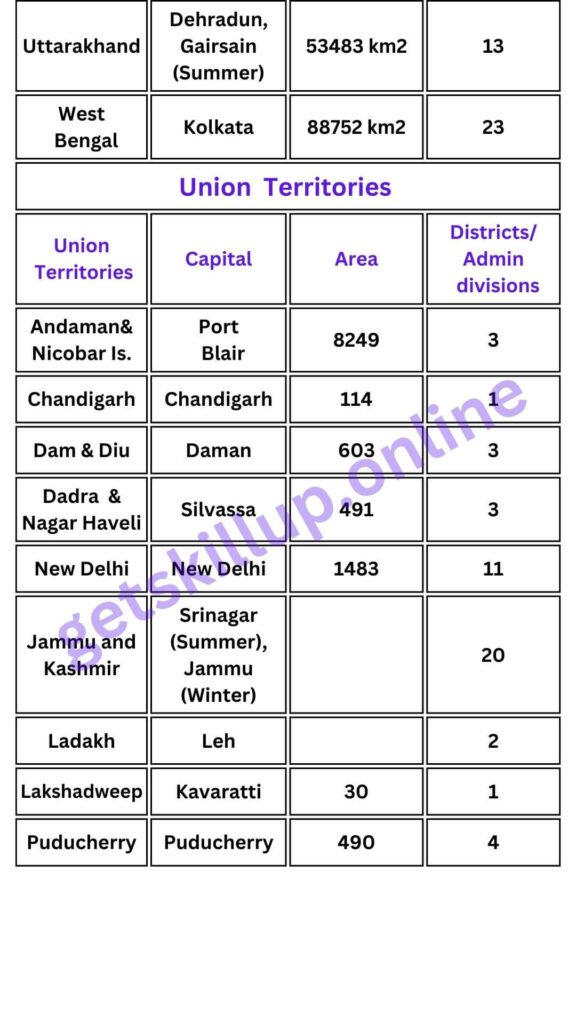
- Administrative divisions of India 28 states and 8 Union Territories
- Independence of India on 15thAugust 1947 (From the British Colonial Rule)
- The Constitution of India came to force on 26thJanuary 1950
- The Constitution of India is the fountain source of the legal system in the Country.
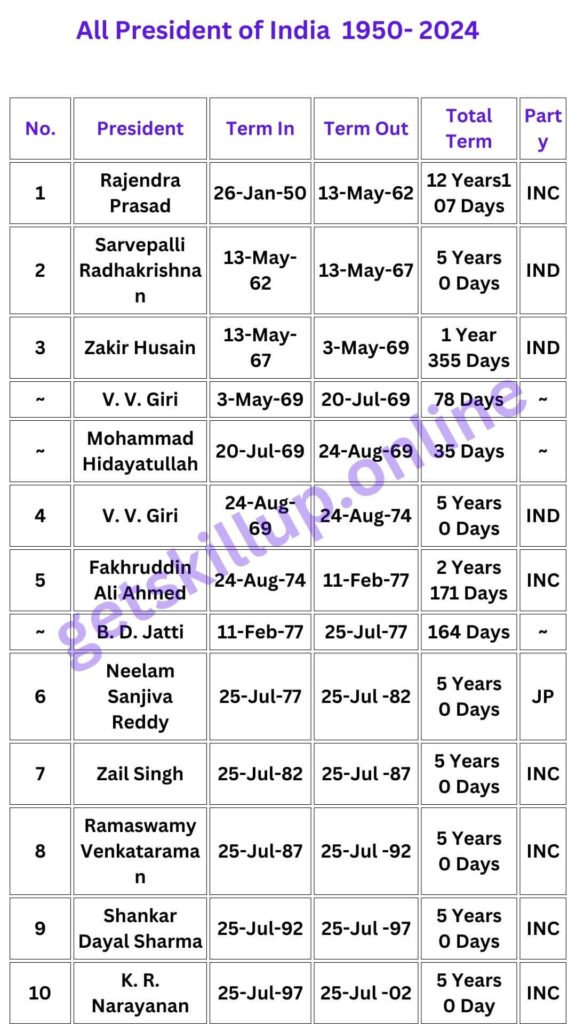
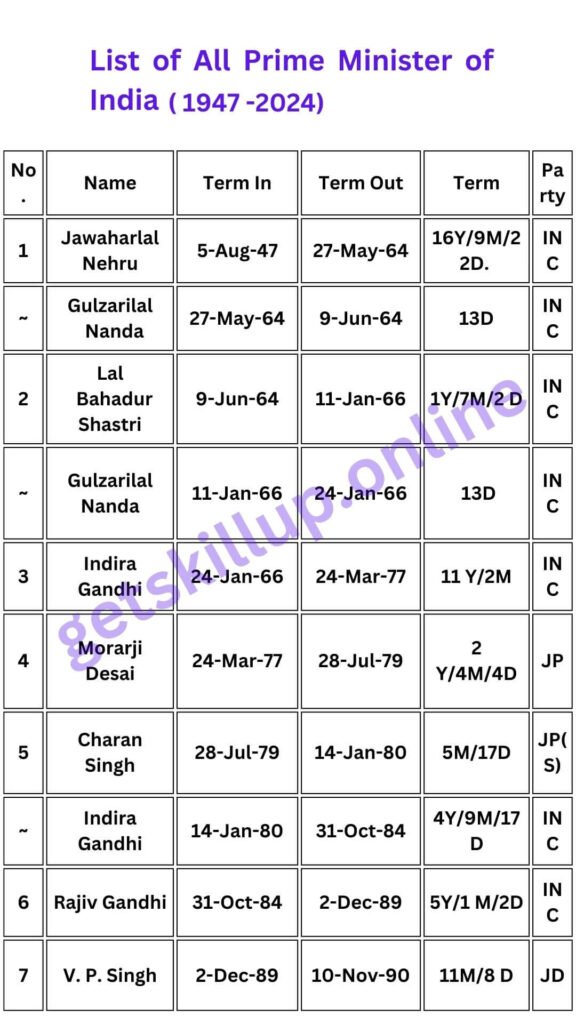
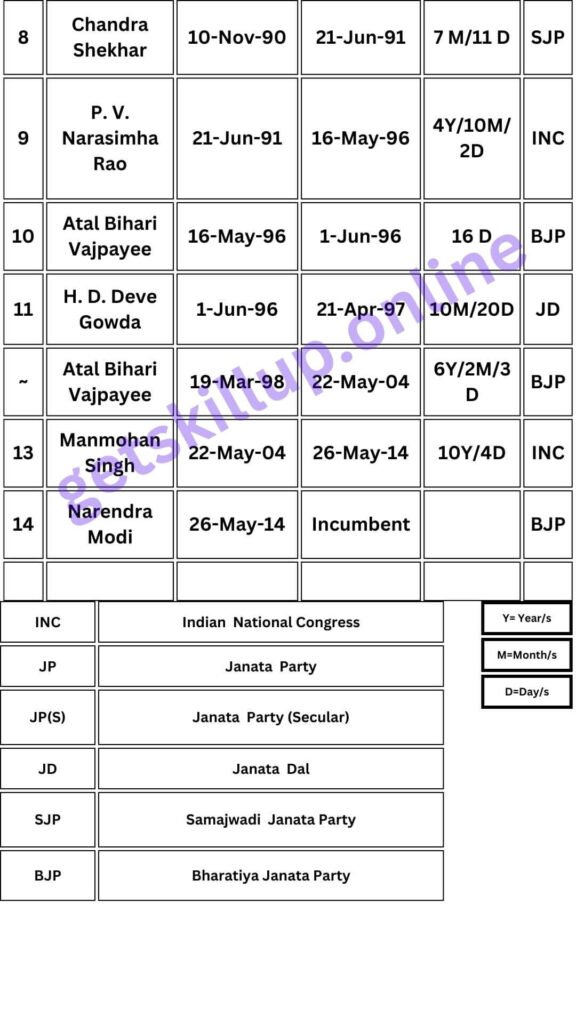
- Executive Branch : The President of India is the Head of the State, while the Prime Minister is the Head of the Government, and runs office with the support of the Council of Ministers who form the Cabinet Ministry.
- Legislative Branch: The Indian Legislature comprises of the Lok Sabha(House of the People) and the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) forming both the Houses of the Parliament
- Judicial Branch: The Supreme Court of India is the apex body of the Indian legal system, followed by other High Courts and subordinate.