1. Fill in the blanks.
(a) Most liquids that conduct electricity are solutions of ______________ and ______________.
(b) The passage of an electric current through a solution causes ______________ effects.
(c) If you pass current through copper sulphate solution, copper gets deposited on the plate connected to the ___________terminal of the battery.
(d) The process of depositing a layer of any desired metal on another material by means of electricity is called _________.
Ans:
(a) acids, bases and salts.
(b) chemical
(c) negative .
(d) electroplating.
2. When the free ends of a tester are dipped into a solution, the magnetic needle shows deflection. Can you explain the reason?
Ans:
When the free ends of a tester are dipped into a solution, the current flows through the solution if it is conductive. This current creates a magnetic field that causes the compass needle to deflect, indicating the solution is conducting electricity.
3. Name three liquids, which when tested in the manner shown in Fig.14.9, may cause the magnetic needle to deflect.
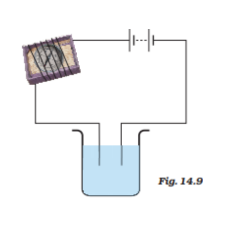
Ans:
Saltwater
Lemon juice
III. Vegetable oil
These liquids can be taken in a beaker to show the passage of electricity, as they will show a deflection in the magnetic needle.
4. The bulb does not glow in the setup shown in Fig.14.10. List the possible reasons. Explain your answer.
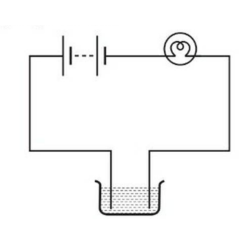
Ans:
The bulb may not glow due to the following reasons:
Non-conducting liquid: If the liquid is non-conductive, the circuit will be incomplete, and current will not flow through the liquid, preventing the bulb from glowing.
Weak electric current: If the circuit is made of materials that are poor conductors, or if the battery does not provide enough energy, the current may be too weak to light the bulb.
5. A tester is used to check the conduction of electricity through two liquids, labelled A and B. It is found that the bulb of the tester glows brightly for liquid A, while it glows very dimly for liquid B. You would conclude that
(i) liquid A is a better conductor than liquid B.
(ii) liquid B is a better conductor than liquid A.
(iii) both liquids are equally conducting.
(iv) conducting properties of liquid cannot be compared in this manner.
Ans:
Liquid A is a better conductor than liquid B.
The brightness of the bulb in the tester is directly related to the amount of current flowing through the liquid. A brighter glow indicates a higher current flow, which happens when the liquid has a higher conductivity. Since liquid A causes a brighter glow, it is more conductive than liquid B, which causes a dimmer glow.
6. Does pure water conduct electricity? If not, what can we do to make it conduct?
Ans:
Pure water does not conduct electricity because it lacks ions necessary for electrical conduction. To make it conduct, we can add a small amount of salt (such as sodium chloride, NaCl), which dissociates into ions and allows current to flow through the water.
7. In case of a fire, before the firemen use the water hoses, they shut off the main electrical supply for the area. Explain why they do this.
Ans:
Before using water hoses in a fire situation, firemen shut off the electrical supply to prevent electrical hazards. Water is a good conductor of electricity, and if it comes into contact with electrical wires or appliances, it could lead to electric shocks, endangering the firemen’s safety.
8. A child staying in a coastal region tests the drinking water and also seawater with his tester. He finds that the compass needle deflects more in the case of seawater. Can you explain the reason?
Ans:
Seawater contains a higher concentration of dissolved salts compared to drinking water. These salts dissociate into ions, which help conduct electricity. Since seawater has more ions, it allows more current to flow, making it a better conductor than drinking water. This results in a greater deflection of the compass needle when testing seawater compared to drinking water.
9. Is it safe for the electrician to carry out electrical repairs outdoors during heavy downpours? Explain.
Ans:
No, it is not safe for an electrician to carry out electrical repairs outdoors during heavy downpours. Rainwater contains dissolved salts, which make it conductive. If the electrician comes into contact with water while repairing electrical appliances, there is a risk of electric shock. The conductivity of the water increases the likelihood of current passing through the electrician’s body, which can be dangerous. Therefore, electrical repairs should only be carried out in dry conditions to prevent harm.
10. Paheli had heard that rainwater is as good as distilled water. So she collected some rainwater in a clean glass tumbler and tested it using a tester. To her surprise, she found that the compass needle showed deflection. What could be the reasons?
Ans:
Rainwater contains dissolved salts and minerals, which make it conductive. These dissolved substances allow electrical current to pass through the water, causing the deflection of the compass needle when tested with a tester. Hence, rainwater is not as pure as distilled water, which is free from such impurities.
11. Prepare a list of objects around you that are electroplated.
Ans:
Chromium plating: Used on exterior parts of automobiles for a shiny, durable surface.
Gold plating: Silver jewelry often has a thin layer of gold, known as gold-plated ornaments.
Zinc plating: Iron objects used in construction are coated with zinc to prevent rusting and corrosion.
12. The process that you saw in Activity 14.7 is used for the purification of copper. A thin plate of pure copper and a thick rod of impure copper are used as electrodes. Copper from the impure rod is sought to be transferred to the thin copper plate. Which electrode should be attached to the positive terminal of the battery and why?
Ans:
The thick rod of impure copper should be attached to the positive terminal of the battery. This is because, during the electrolysis process, copper from the impure rod (anode) dissolves into the solution, and copper ions are then reduced at the thin copper plate (cathode) to form pure copper. The impure copper rod loses copper atoms, which are replaced by pure copper from the solution, making it the positive electrode.
