1. Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
(float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation)
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _____________.
(b) The first step before growing crops is _____________ of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would _____________ on top of water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and _____________ and _____________ from the soil are essential.
Ans:
(a)crop. (b) preparation. (c) float. (d) water and nutrients.
2. Match items in column A with those in column B.

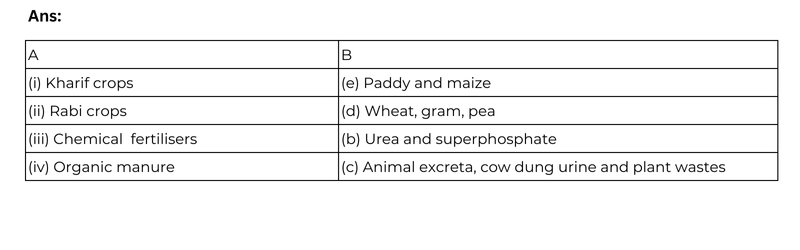

2. Match items in column A with those in column B.


3. Give two examples of each.
Ans:
(a) Kharif crops: Paddy and maize
(b) Rabi crops: Wheat and pea
4. Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following:
(a) Preparation of soil
(b) Sowing
(c) Weeding
(d) Threshing
Ans: (a) Preparation of soil
Preparation of soil is the first and most crucial step in agriculture. It involves loosening and turning the soil to allow roots to penetrate deeper and breathe easily. Loosened soil improves aeration and facilitates the growth of earthworms and microorganisms, which enhance soil fertility by adding humus. This process also brings nutrient-rich soil to the surface, which is vital for plant growth and ensures better water absorption.
(b) Sowing
Sowing is a significant step in crop production. It begins with the selection of healthy and high-quality seeds to ensure good crop yield. Sowing can be done using traditional methods, such as broadcasting seeds by hand, or modern methods using a seed drill. The seed drill ensures uniform seed distribution and proper depth placement, which helps in better germination and growth of the crop.
(c) Weeding
Weeding is the process of removing unwanted plants, called weeds, from the field. Weeds compete with crops for nutrients, water, and sunlight, which reduces crop yield. They also hinder harvesting and can be harmful to both humans and animals if poisonous. Weeding can be done manually by uprooting weeds or by tilling the soil. Additionally, chemical weedicides are used to kill weeds, but caution is necessary as these chemicals may harm the health of farmers.
(d) Threshing
Threshing is the process of separating grains from the chaff or husks after harvesting. It is usually carried out using a machine called a combine, which acts as both a harvester and a thresher. Alternatively, winnowing is used, where air is blown to separate the lighter chaff from the heavier grains. Threshing ensures the grains are ready for further processing or storage.
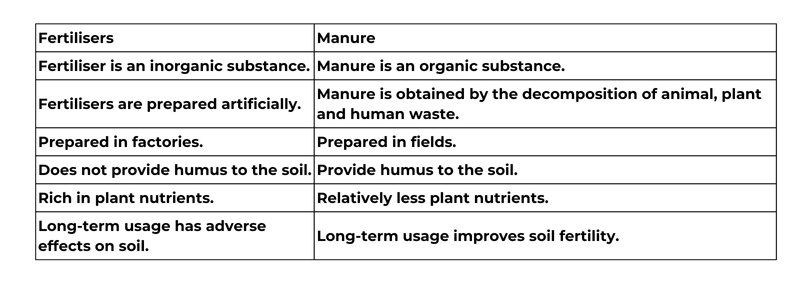
5. Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
6. What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Ans: The process of supplying water to crops at regular intervals is called irrigation. It is essential for plant growth, especially in areas with insufficient rainfall.
Methods of irrigation which conserve water:
a) Drip Irrigation:
In this method, water is delivered drop by drop directly to the roots of plants through a system of pipes and emitters. This ensures minimal water wastage and reduces evaporation and runoff. Drip irrigation is particularly effective in conserving water and preventing weed growth, as water is provided only to the plant roots.
b) Sprinkler System:
This method is used mainly on uneven land where water availability is limited. The system consists of perpendicular pipes fitted with rotating nozzles that spray water over the crops like rainfall. Water is distributed uniformly under pressure, reducing water wastage and ensuring efficient irrigation
7. If wheat is sown in the Kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Ans: Wheat is a Rabi crop and requires cool temperatures for proper growth. If wheat is sown in the Kharif season, it will likely fail to grow or yield properly due to the following reasons:
Unfavorable temperature: Kharif season is characterized by hot and humid weather, which is unsuitable for wheat growth.
Excessive rainfall: Wheat cannot survive in waterlogged soil conditions caused by heavy rainfall during the Kharif season.
Pests and diseases: High moisture levels during this season create favorable conditions for pests and diseases, which may destroy the wheat crop.
Thus, wheat crops are better suited for the Rabi season when the climate is cooler and dry.
8. Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Ans: Continuous plantation of crops in the same field adversely affects the soil due to the following reasons:
Depletion of nutrients: Plants extract nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium from the soil for their growth. Continuous plantation depletes these essential nutrients without giving the soil time to replenish them.
Loss of fertility: The soil becomes infertile over time, leading to reduced crop yields.
Soil erosion: Continuous cultivation may disturb the soil structure, increasing the chances of erosion.
To maintain soil fertility, crop rotation, fallowing, or adding fertilizers and organic manure is essential.
9. What are weeds? How can we control them?
Ans: Weeds are undesirable plants that grow naturally alongside the main crop in a field. They compete with crops for sunlight, water, nutrients, and space, reducing the crop yield.
Methods to control weeds:
Tilling: Plowing the field before sowing uproots the weeds, and they get mixed with the soil.
Manual removal: Weeds can be physically uprooted by hand or using tools like a hoe.
Weedicides: Certain chemicals like 2,4-D can be sprayed to kill weeds without harming the crop.
Crop rotation: Growing different types of crops in succession prevents the growth of specific weeds.
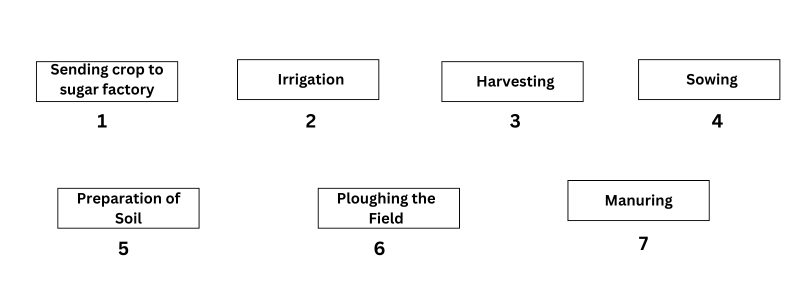
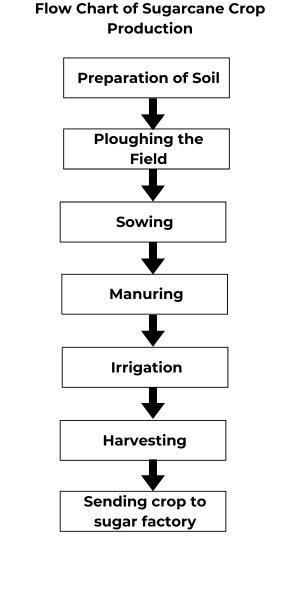
10. Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.
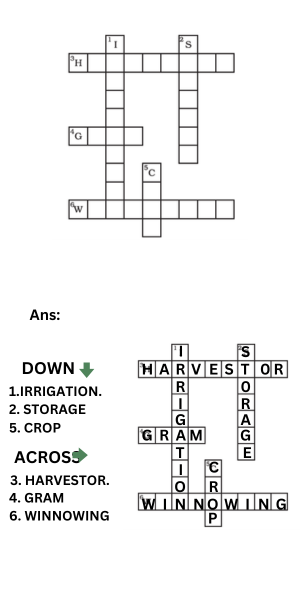
11. Complete the following word puzzle with the help of the clues given below.
Down
Providing water to the crops.
Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper conditions.
Certain plants of the same kind are grown on a large scale.
Across
A machine used for cutting the matured crop.
A rabi crop, which is also one of the pulses.
A process of separating the grain from the chaff.