1. What is meant by a substance?
Ans: A substance is a type of matter composed of particles that cannot be separated by any physical process because all its constituent particles are uniform and possess the same chemical properties.
Examples of substances include elements (e.g., gold, oxygen) and compounds (e.g., water, carbon dioxide).
2. List the points of differences between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.

3. Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures with examples.

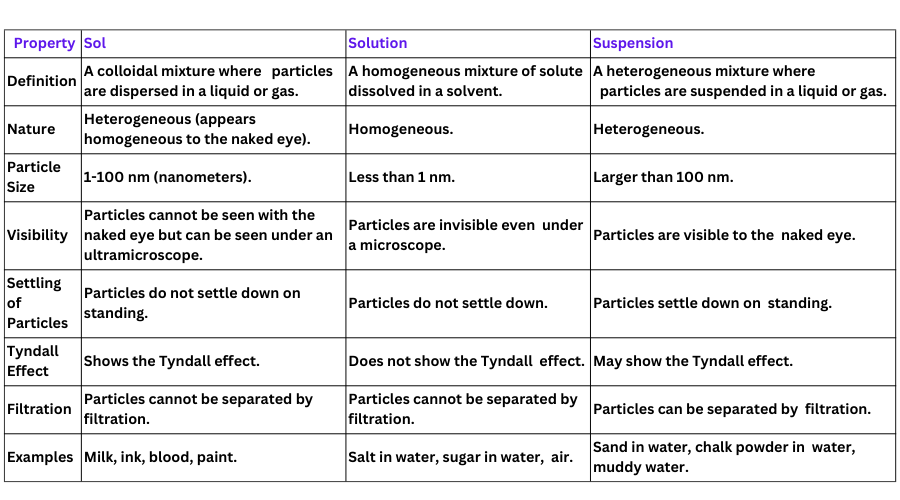
4. How are sol, solution and suspension different from each other?
5. To make a saturated solution, 36 g of sodium chloride is dissolved in 100 g of water at 293 K. Find its concentration at this temperature.
Solution :
Mass of sodium chloride (solute) = 36 g
Mass of water (solvent) = 100 g
Mass of solution = 36 + 100 = 136 g
Therefore, concentration percentage = mass of solute/mass of solution
= 26.47 %
6. How will you separate a mixture containing kerosene and petrol (difference in their boiling points is more than), which are miscible with each other?
Ans:
To separate a mixture of kerosene and petrol (which are miscible liquids with a significant difference in their boiling points), the distillation technique is used.
Explanation:
Principle: Distillation is based on the difference in boiling points of the liquids.
Petrol has a lower boiling point compared to kerosene.
Process:
The mixture is heated in a distillation apparatus.
Petrol, being more volatile, evaporates first and is collected as a liquid after condensation.
Kerosene, with a higher boiling point, remains in the distillation flask and is collected later.
Conclusion:
Through distillation, petrol and kerosene are separated based on their difference in boiling points.
7. Name the technique to separate
(i) butter from curd,
(ii) salt from sea-water,
(iii) camphor from salt.
Ans:
(i) centrifugation method.
(ii) evaporation method.
(iii) sublimation method.
8. What type of mixtures are separated by the technique of crystallisation?
Ans: Crystallisation is used to separate pure solids from their impure samples.
Examples:
Purifying sugar from an impure sample.
Obtaining salt from seawater.
Separating copper sulfate crystals.
9. Write the steps you would use for making tea. Use the words solution, solvent, solute, dissolve, soluble, insoluble, filtrate and residue.
Ans:
Take water (solvent) in a pan and heat it.
Add sugar (solute) to the solvent; it will dissolve completely, forming a true solution.
Add tea leaves (insoluble) and milk (another soluble liquid).
Boil the mixture.
Filter it using a sieve; the filtrate is tea, and the residue is the tea leaves, which are discarded.
10. Classify the following as chemical or physical changes
- cutting of trees,
- melting of butter in a pan,
- rusting of almirah,
- boiling of water to form steam,
- passing of electric current, through water and the water breaking down into hydrogen and oxygen gases,
- dissolving common salt in water,
- making a fruit salad with raw fruits, and
- burning of paper and wood.
