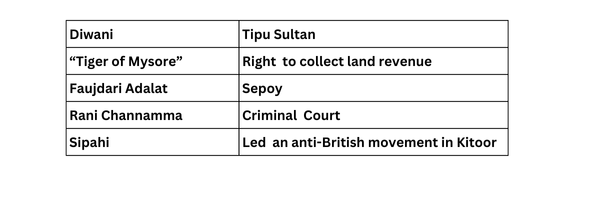
1. Match the following:
2. Fill in the blanks:
(a) The British conquest of Bengal began with the Battle of ___________.
(b) Haidar Ali and Tipu Sultan were the rulers of ___________.
(c) Dalhousie implemented the Doctrine of ___________.
(d) Maratha kingdoms were located mainly in the ___________ part of India.
Ans.
(a) Plassey
(b) Mysore.
(c) Lapse
(d) South-western
3. State whether true or false:
(a) The Mughal empire became stronger in the eighteenth century.
(b) The English East India Company was the only European company that traded with India.
(c) Maharaja Ranjit Singh was the ruler of Punjab.
(d) The British did not introduce administrative changes in the territories they conquered.
Ans.
(a False
(b) False
(c) True
(d) False
4. What attracted European trading companies to India?
Ans:
European trading companies sought new territories where they could purchase goods at low prices and sell them in Europe for high profits. India’s fine-quality cotton and silk had a significant demand in European markets. Additionally, spices like pepper, cloves, cardamom, and cinnamon were highly sought after. These factors drew European trading companies to India.
5. What were the areas of conflict between the Bengal nawabs and the East India Company?
Ans:
After establishing their first factory in 1651 on the river Hugli, the East India Company began bringing in more merchants and traders to Bengal. Conflicts arose between the Bengal nawabs and the East India Company due to the following reasons:
a. Nawabs refused to grant the Company certain concessions
b. Nawabs demanded hefty tributes from the Company
c. The Company resisted paying taxes
d. Company officials addressed the nawabs disrespectfully
6. How did the assumption of Diwani benefit the East India Company?
Ans:
Diwani rights granted the British authority to collect revenue and manage civil cases. This greatly benefited the East India Company:
a. It provided access to Bengal’s vast revenue resources
b. The Company gained complete control over trade in the region
c. Bengal’s revenues were used to export Indian goods abroad
7. Explain the system of “subsidiary alliance.”
Ans:
The system of subsidiary alliance required Indian rulers to disband their armed forces and accept East India Company protection. Key changes under this system were:
a. The East India Company took charge as the protector of allied territories
b. An English resident was posted to monitor the ruler’s activities
c. Indian rulers were forbidden from allowing other European powers to trade or enter their territories
d. Indian rulers had to fund the Company’s subsidiary forces, and failure to do so resulted in losing their territories to the Company
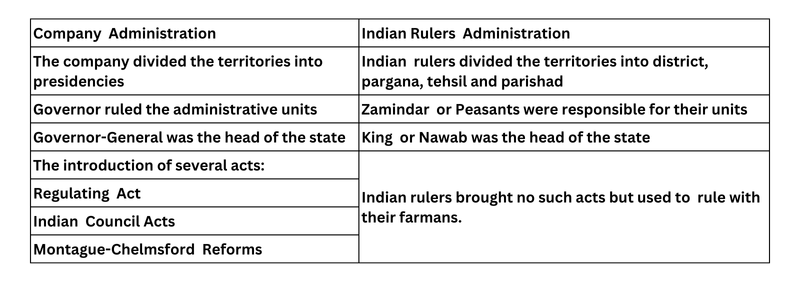
8. In what way was the administration of the Company different from that of Indian rulers?
Ans.
The difference in the administration of the company and that of the Indian rulers is given below:
9. Describe the changes that occurred in the composition of the Company’s army.
Ans:
The East India Company’s army, called the Sepoy Army, was mainly composed of Indian peasants who were trained to become professional soldiers. A significant change in the army was the shift in dominance from cavalry to infantry due to the use of muskets and matchlocks for protection. The Company also established a uniform military culture, providing European-style training through drills and other exercises.
