1. Which of the following cannot be charged easily by friction?
(a) A plastic scale
(b) A copper rod
(c) An inflated balloon
(d) A woollen cloth.
Ans:
(b) A copper rod.
2. When a glass rod is rubbed with a piece of silk cloth, the rod
(a) and the cloth both acquire a positive charge.
(b) becomes positively charged while the cloth has a negative charge.
(c) and the cloth both acquire a negative charge.
(d) becomes negatively charged while the cloth has a positive charge.
Ans:
(b) becomes positively charged while the cloth has a negative charge.
3. Write T against true and F against false in the following statements.
(a) Like charges attract each other. (T/F)
(b) A charged glass rod attracts a charged plastic straw. (T/F)
(c) Lightning conductors cannot protect a building from lightning. (T/F)
(d) Earthquakes can be predicted in advance. (T/F)
Ans:
a) False – Unlike charges attract each other, while like charges repel each other.
b) True – A charged plastic straw has a negative charge on its surface, while the glass rod has a positive charge on its surface. Unlike charges attract each other, so they attract each other.
c) False – Lightning conductors protect buildings by providing a path for the atmospheric charges to flow directly to the earth, preventing damage from lightning.
d) False – Although the causes of earthquakes are known, no reliable instruments exist to predict earthquakes in advance. Therefore, they cannot be predicted in advance.
4. Sometimes, a crackling sound is heard while taking off a sweater during winter. Explain.
Ans:
The crackling sound occurs due to static electricity. When we take off a woollen sweater, friction between the sweater and our body causes the transfer of electrons, charging the sweater. This results in a sudden discharge of electricity, creating the crackling sound.
5. Explain why a charged body loses its charge if we touch it with our hand.
Ans:
When a charged body is touched, the charge is transferred to our body, which is a good conductor. From there, the charge flows to the earth, neutralizing the body. This process is called electric discharge, and it results in the loss of charge from the body.
6. Name the scale on which the destructive energy of an earthquake is measured. An earthquake measures 3 on this scale. Would it be recorded by a seismograph? Is it likely to cause much damage?
Ans:
The destructive energy of an earthquake is measured on the Richter scale, which ranges from 1 to 10.
An earthquake with a magnitude of 3 would indeed be recorded by a seismograph, as even small tremors are detectable.
However, an earthquake with a magnitude of 3 is generally too weak to cause significant damage. Earthquakes of magnitude 5 or higher are typically considered capable of causing noticeable damage.
7. Suggest three measures to protect ourselves from lightning.
Ans:
Here are three measures to protect ourselves from lightning:
(i) Stay indoors: Always remain inside a building during a lightning storm. If you are in a car, stay inside with the windows closed, as cars provide some protection from lightning.
(ii) Avoid contact with conductive materials: Never touch electrical wires, telephone cables, metal pipes, or any objects that could conduct electricity during a storm.
(iii) Avoid water: Do not bathe, shower, or use running water during a lightning storm, as water is a good conductor and can increase the risk of electric shock.
8. Explain why a charged balloon is repelled by another charged balloon, whereas an uncharged balloon is attracted by another charged balloon.
Ans:
When both balloons are charged with the same type of charge (either positive or negative), they repel each other because like charges repel. However, when a charged balloon is brought near an uncharged balloon, the uncharged balloon experiences charge induction. The side of the uncharged balloon closest to the charged balloon becomes oppositely charged, while the far side remains positively charged. As opposite charges attract, the charged balloon attracts the uncharged one.
9. Describe with the help of a diagram an instrument which can be used to detect a charged body.
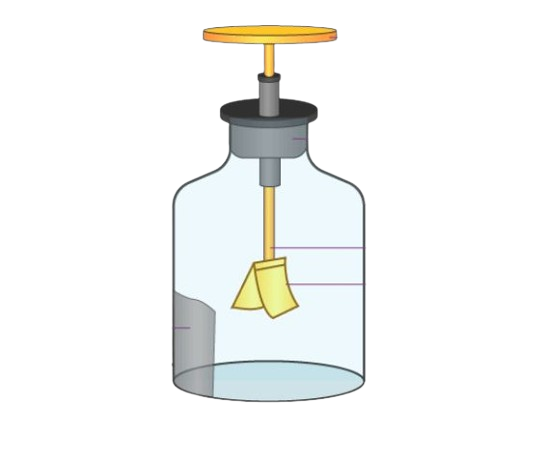
Ans:
An instrument used to detect a charged body is called an electroscope. It consists of a metal rod with two aluminum foil leaves at one end and a metal disc at the other. The entire setup is placed inside a glass flask, and the flask is corked to isolate it from external air.
When a charged object touches the metal disc, the charge transfers to the leaves via conduction. As both leaves acquire the same charge, they repel each other, and the degree of repulsion can be used to detect the presence of charge. If no charge is present, the leaves will remain attracted to each other.
10. List three states in India where earthquakes are more likely to strike.
Ans:
Earthquakes are more likely to strike in the following states in India:
Gujarat
Assam
Jammu & Kashmir
These areas are more prone to seismic activity due to their proximity to tectonic plate boundaries.
11. Suppose you are outside your home, and an earthquake strikes. What precautions would you take to protect yourself?
Ans:
The following precautions should be taken when an earthquake strikes:
(a) Move to an open space: Find an open field or an open area away from buildings, trees, electric wires, and poles, as they can collapse or fall during the earthquake.
(b) Stay inside a car if you’re in one: If you are inside a car, drive to an open space, and stay inside the car until the earthquake stops. Avoid stopping under bridges or near large trees or electrical poles.
12. The weather department has predicted that a thunderstorm is likely to occur on a certain day. Suppose you have to go out on that day. Would you carry an umbrella? Explain.
Ans:
No, one should not carry an umbrella during a thunderstorm. Thunderstorms are often accompanied by lightning, and if the umbrella has a metal rod, the charges may travel from the cloud through the metal, potentially causing an electric shock to the person holding it. To stay safe, it is best to avoid carrying an umbrella during a thunderstorm.
