1. Fill in the blanks.
(a) A place where animals are protected in their natural habitat is called a _________.
(b) Species found only in a particular area are known as _______.
(c) Migratory birds fly to faraway places because of __________ changes.
Ans:
(a) sanctuary.
(b) endemic.
(c) climatic.
2. Differentiate between the following.
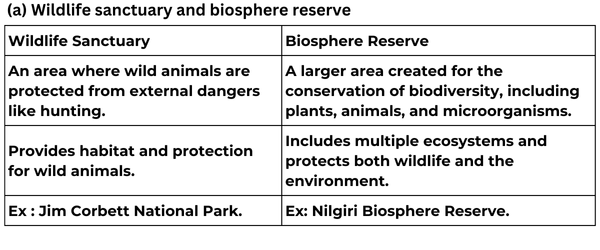
(a) Wildlife sanctuary and biosphere reserve
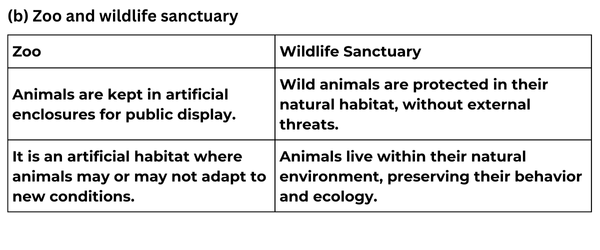
(b) Zoo and wildlife sanctuary
(c) Endangered and extinct species
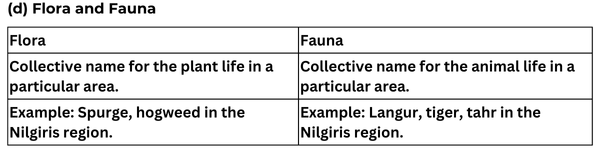
(d) Flora and fauna
(a) Wildlife sanctuary and biosphere reserve
(b) Zoo and wildlife sanctuary
(c) Endangered and extinct species

(d) Flora and fauna
3. Discuss the effects of deforestation on the following.
Ans:
(a) Wild animals
Deforestation destroys the natural habitats of wild animals, threatening their existence. Without plant life, animals lose their shelter, food sources, and protection, leading to the possible extinction of species.
(b) Environment
Deforestation increases carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, contributing to global warming. This disrupts the water cycle, changing rainfall patterns and causing droughts and floods. The loss of vegetation also reduces oxygen levels and harms biodiversity.
(c) Villages (Rural areas)
In rural areas, deforestation leads to soil erosion, which strips the land of fertility, making it harder for farmers to grow crops. The loss of plant cover also contributes to water scarcity and increased vulnerability to natural disasters like floods.
(d) Cities (Urban areas)
In cities, deforestation exacerbates global warming due to the increased CO2 levels. It also disrupts the water cycle, leading to unpredictable weather patterns, including floods and droughts. The urban heat island effect is worsened by the loss of vegetation.
(e) Earth
On a global scale, deforestation accelerates desertification, soil erosion, and the greenhouse effect. The loss of biodiversity reduces the planet’s ability to recover from environmental stress. The Earth faces an increased risk of natural calamities and climate instability.
(f) The next generation
The next generation will inherit a planet with degraded ecosystems, reduced biodiversity, and harsher climate conditions. They will face challenges such as food insecurity, water scarcity, and the impacts of climate change, all exacerbated by deforestation.
4. What will happen if
Ans:
(a) We go on cutting trees
Continued deforestation will lead to habitat destruction for wildlife, increased global warming, soil erosion, and disruption of the water cycle. This will result in higher risks of droughts, floods, and natural disasters.
(b) The habitat of an animal is disturbed
Disturbing an animal’s habitat forces it to relocate, often leading to difficulties in finding food, water, and shelter. This can increase the risk of conflict with humans or other animals and can even result in the death of the animal.
(c) The top layer of soil is exposed
Exposing the topsoil to wind and water leads to soil erosion, which removes the fertile topsoil. This makes the land less productive, reducing agricultural yields and increasing desertification over time.
5. Answer in brief.
Ans:
(a) Why should we conserve biodiversity?
Biodiversity is essential for maintaining ecological balance. Plants, animals, and microorganisms are interconnected and depend on each other for survival. Conserving biodiversity ensures the sustainability of ecosystems, food sources, and natural resources.
(b) Protected forests are also not completely safe for wild animals. Why?
Even in protected forests, human activities like poaching, deforestation, and habitat destruction threaten wild animals. The encroachment of human populations can lead to the exploitation of wildlife, putting animals at risk.
(c) Some tribals depend on the jungle. How?
Tribals rely on forests for food, shelter, medicine, and raw materials like wood for fuel. They also depend on forests for their cultural practices and livelihoods.
(d) What are the causes and consequences of deforestation?
Causes: Urbanization, agricultural expansion, logging, and demand for firewood. Consequences: Soil erosion, loss of biodiversity, increased greenhouse gases, global warming, altered water cycles, floods, and droughts.
(e) What is the Red Data Book?
The Red Data Book is a catalog maintained by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) that lists endangered and threatened plant and animal species. It serves as a critical tool for conservation efforts.
(f) What do you understand by the term migration?
Migration refers to the seasonal or periodic movement of animals or organisms from one habitat to another, often for breeding, food, or more favorable climatic conditions.
6. In order to meet the ever-increasing demand in factories and for shelter, trees are continually being cut. Is it justified to cut trees for such projects? Discuss and prepare a brief report.
Ans: No, it is not justified to cut trees to meet the demands of urban expansion. Trees play an essential role in maintaining the ecological balance by providing oxygen, absorbing CO2, preventing soil erosion, and supporting biodiversity. Deforestation leads to long-term environmental issues like global warming, soil degradation, and climate instability. In the face of such challenges, it is critical to find sustainable alternatives to meet human needs without harming the environment.
7. How can you contribute to the maintenance of the green wealth of your locality?
Ans: Plant trees in your locality and encourage others to do the same.
Organize awareness campaigns about the importance of plants and trees in maintaining ecological balance.
Protect existing trees by ensuring they are watered regularly and not harmed.
Educate children and youth about the importance of conservation.
Create community initiatives for regular tree plantation and maintenance.
8. Explain how deforestation leads to reduced rainfall.
Ans: Deforestation disrupts the water cycle. Plants absorb CO2 and release moisture into the atmosphere through transpiration. When trees are cut, CO2 levels rise, contributing to global warming and altering weather patterns. This disrupts the natural rainfall cycle, leading to reduced rainfall, droughts, and erratic weather patterns.
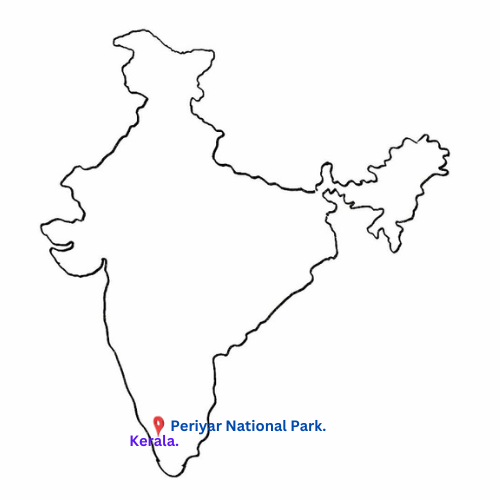
9. Find out about national parks in your state. Identify and show their location on the outline map of India.
10. Why should the paper be saved? Prepare a list of ways by which you can save paper.
Ans:
Soln:
Saving paper is crucial because paper production involves the cutting down of trees, which play a significant role in maintaining ecological balance. For every ton of clean white paper produced, approximately 17 full-grown trees are cut down. These trees contribute to oxygen production, carbon dioxide absorption, and provide habitat for wildlife. By saving paper, we reduce deforestation, help conserve biodiversity, and mitigate environmental issues such as climate change.
Ways to save paper: Collection and recycling of used paper: Recycle paper to avoid the need for new paper production, thus saving trees.
Using both sides of a paper for writing: Maximize the use of paper by using both sides for writing or printing.
Spreading awareness: Educate school children and youth about the importance of saving paper and its impact on the environment.
Intelligent and proper use of paper: Avoid unnecessary printing and use paper only when needed. Reuse scrap paper for notes or drafts.
Digital alternatives: Opt for digital documentation, email, or electronic files instead of printing papers when possible.
Purchase recycled paper: Use paper products made from recycled materials to reduce the demand for new paper.
Buy paper in bulk: Reduce packaging waste and the need for excess paper consumption by buying in bulk.
Donate old books and papers: Donate unwanted books and papers instead of discarding them, encouraging reuse and reducing waste.
By adopting these practices, we can contribute to the conservation of trees and help protect the environment.
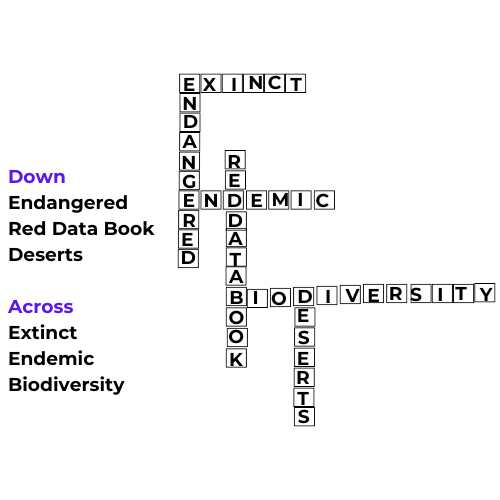
11. Complete the word puzzle.
Down
Species on the verge of extinction.
A book carrying information about endangered species.
Consequences of deforestation.
Across
Species which have vanished.
Species found only in a particular habitat.
Variety of plants, animals and microorganisms found in an area.
diagram
2. Differentiate between the following.
